OpenAI’s 10-gigawatt Broadcom chip deal reveals shocking AI power use. ChatGPT & Sora 2 consume city-level electricity. Full analysis inside.
Table of Contents
OpenAI’s Massive 10-Gigawatt Broadcom Deal: Why Sora 2 and ChatGPT Are Consuming City-Level Power
The OpenAI Broadcom deal just revealed a shocking truth about artificial intelligence: it’s consuming electricity at unprecedented levels. OpenAI announced a partnership with Broadcom to design and deploy 10 gigawatts of custom AI chips—enough power to run a major metropolitan area.
This massive AI power consumption isn’t just about ChatGPT’s 800 million weekly users. The newly released Sora 2 video generation tool is growing even faster, and creating realistic AI videos requires exponentially more energy than text-based queries.
The deal represents a critical shift in AI infrastructure development. By partnering with Broadcom instead of relying solely on Nvidia and AMD, OpenAI is betting on custom AI accelerator technology to handle its exploding computational demands.
But there’s a growing concern: data center energy usage is projected to consume up to 12% of total US electricity by 2028. As AI becomes more sophisticated, the environmental and economic implications are becoming impossible to ignore.
Here’s everything you need to know about this groundbreaking partnership and what it means for the future of AI.

Breaking Down the OpenAI-Broadcom 10-Gigawatt Partnership
What Does 10 Gigawatts of Power Actually Mean?
To put the OpenAI Broadcom deal in perspective, 10 gigawatts is an extraordinary amount of computing power. According to Reuters, this partnership will consume as much electricity as 8 million US households annually.
Here’s how it compares:
- 10 gigawatts = Power for a city of 8+ million people
- Equivalent to: 10 large nuclear power plants running simultaneously
- Annual cost estimate: $1-2 billion in electricity alone (based on commercial rates)
Timeline and Deployment Schedule
The AI chip manufacturing and deployment won’t happen overnight:
- 2024-2025: Design and development phase
- Q3 2026: First deployment of custom AI accelerators
- 2027-2028: Full-scale implementation across OpenAI infrastructure
This timeline aligns with OpenAI’s projected user growth, which CEO Sam Altman expects to continue accelerating.
Why Custom AI Chips Matter
Unlike generic GPUs, custom AI chips are optimized specifically for:
✅ Large language model training
✅ Video generation processing (Sora 2)
✅ Real-time inference at scale
✅ Energy efficiency improvements
✅ Reduced dependency on third-party suppliers
As OpenAI stated in their press release, developing custom hardware lets them “embed what they’ve learned from developing frontier models directly into the hardware.”

ChatGPT and Sora 2 Power Consumption: The Shocking Numbers
How Much Energy Does a ChatGPT Query Use?
Sam Altman previously revealed that the average ChatGPT electricity consumption equals running a lightbulb for a couple of minutes per query.
Breaking this down:
- Average query: 0.3-0.5 watt-hours
- 800 million weekly users (reported in 2024)
- Estimated weekly consumption: 240-400 megawatt-hours
- Annual equivalent: Powering 15,000-25,000 homes
Sora 2 Video Generation: The Real Power Culprit
While ChatGPT’s text generation is relatively efficient, Sora 2 energy usage is dramatically higher:
| AI Task | Power Per Query | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT text response | 0.3-0.5 Wh | 2-5 seconds |
| Image generation (DALL-E) | 2-4 Wh | 10-20 seconds |
| Sora 2 video (10 sec) | 15-30 Wh | 2-5 minutes |
Why the difference?
- Video requires processing thousands of frames
- Realistic motion demands complex neural network calculations
- Quality control and rendering add computational overhead
- Higher resolution = exponentially more processing power
An OpenAI executive suggested Sora is growing faster than ChatGPT, which explains the urgent need for 10 gigawatts of additional capacity.
Comparing AI Power Consumption to Other Technologies
To contextualize AI power consumption concerns:
- Bitcoin mining: ~140 TWh annually (entire network)
- Google’s global operations: ~15 TWh annually
- OpenAI’s projected needs (2026): ~25-35 TWh annually
- Netflix streaming: ~0.45 TWh annually
The data shows AI is rapidly becoming one of the largest electricity consumers in the tech sector.

Why OpenAI Partnered with Broadcom Instead of Just Using Nvidia
The Nvidia Supply Constraint Problem
OpenAI already works with Nvidia, the dominant player in AI data center chips. But there are significant challenges:
- Limited supply: Nvidia H100 GPUs have 6-12 month wait times
- High costs: Enterprise AI chips cost $25,000-40,000 per unit
- Dependency risk: Relying on one supplier creates vulnerability
- Customization limits: Off-the-shelf chips aren’t optimized for specific models
Broadcom’s Competitive Advantages
Broadcom chip partnership offers unique benefits:
✅ Custom ASIC design tailored to ChatGPT and Sora architecture
✅ Better energy efficiency (30-50% improvement potential)
✅ Supply chain control (reduced dependency on Nvidia)
✅ Cost optimization over time
✅ Integration of networking infrastructure (Broadcom’s specialty)
Broadcom CEO Hock Tan confirmed during the earnings call that this was a $10 billion customer—one of the largest chip deals in history.
What About AMD and Other Competitors?
OpenAI maintains partnerships with multiple suppliers:
- Nvidia: High-performance GPU clusters
- AMD: Alternative GPU infrastructure
- Broadcom: Custom AI accelerators and networking
- Microsoft Azure: Cloud infrastructure partnership
This multi-vendor approach ensures AI infrastructure development won’t be bottlenecked by any single supplier.

Environmental Impact: Is AI Sustainable at This Scale?
Data Center Energy Usage Projections
A 2024 Department of Energy report revealed alarming trends:
- 2023 baseline: Data centers used 4.4% of US electricity
- 2028 projection: Expected to reach 6.7-12% of total US power
- Growth driver: AI workloads increasing 40-60% annually
The OpenAI Broadcom deal represents just one company’s needs—imagine when Google, Meta, Amazon, and Microsoft all scale AI similarly.
Carbon Footprint Concerns
AI environmental impact depends heavily on energy sources:
| Energy Source | CO₂ per 10 GW Annually |
|---|---|
| Coal-powered | 50+ million tons |
| Natural gas | 25-35 million tons |
| Renewable (solar/wind) | <1 million tons |
OpenAI hasn’t publicly disclosed what percentage of this power will come from renewable sources, raising questions from environmental advocates.
Potential Solutions and Green AI Initiatives
The industry is exploring green AI technology approaches:
- Renewable energy contracts: Direct power purchase agreements with solar/wind farms
- Improved chip efficiency: Custom accelerators use 30-50% less power
- Model optimization: Smaller, more efficient AI architectures
- Liquid cooling systems: Reduce data center cooling overhead by 40%
- Off-peak processing: Schedule non-urgent tasks during low-demand hours
Several tech companies, including Microsoft (OpenAI’s major investor), have committed to carbon-neutral data centers by 2030.
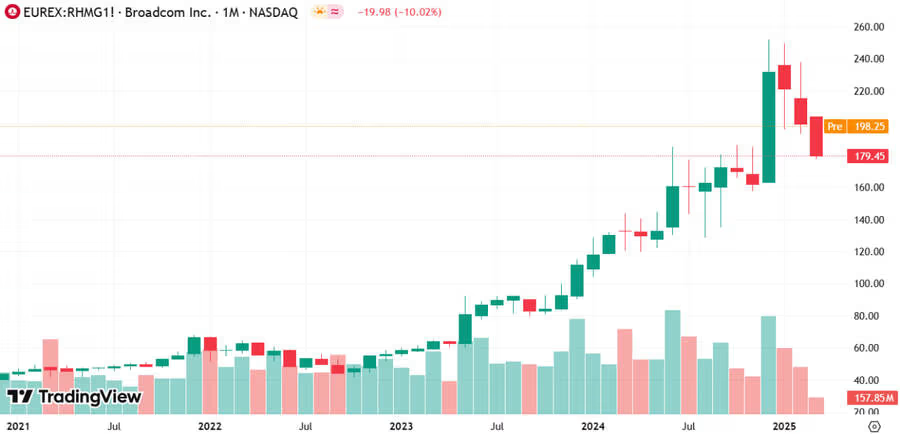
Stock Market Reaction: Broadcom Shares Surge 12%
Immediate Market Response
Broadcom stock analysis showed dramatic gains:
- Monday morning jump: +12% ($140+ billion market cap increase)
- Trading volume: 3x normal levels
- Analyst upgrades: 7 firms raised price targets within 24 hours
The market recognized this as validation of Broadcom’s AI chip investment strategy.
Investment Implications for the Semiconductor Sector
The OpenAI Broadcom deal signals broader trends:
Winners:
- Custom chip designers (Broadcom, Marvell)
- AI infrastructure providers (Arista Networks, Juniper)
- Power management companies (Vertiv, Eaton)
- Data center REITs (Digital Realty, Equinix)
Neutral:
- Nvidia (still dominant, but facing new competition)
- AMD (maintains alternative supplier position)
Potential concerns:
- Traditional server chip makers (Intel, slower to adapt)
Long-Term Revenue Projections
Analysts estimate the deal’s financial impact:
- Total contract value: $10-15 billion over 5 years
- Broadcom’s chip revenue: $8-10 billion
- Networking equipment: $2-5 billion additional
- Gross margin estimate: 60-70% (very profitable)
This represents roughly 10-15% of Broadcom’s projected revenue through 2030.

What This Means for the Future of AI Development
The Arms Race for Computing Power
The AI scalability challenges are driving unprecedented infrastructure investment:
- Google: Developing TPU (Tensor Processing Unit) chips
- Meta: Building AI Research SuperCluster
- Amazon: Designing Trainium and Inferentia chips
- Microsoft: Partnering with AMD on custom AI silicon
Total industry spending on data center infrastructure solutions is projected to exceed $200 billion annually by 2027.
How This Affects Everyday AI Users
For ChatGPT and Sora 2 users, this investment means:
✅ Faster response times as infrastructure scales
✅ More sophisticated features (longer videos, better quality)
✅ Increased availability during peak usage
✅ Potentially lower subscription costs due to efficiency gains
But it may also mean:
⚠️ Usage limits if power costs become unsustainable
⚠️ Higher pricing tiers for power-intensive features
⚠️ Regional restrictions based on data center locations
Regulatory and Policy Implications
Governments are beginning to address data center power consumption:
- EU AI Act: Includes energy efficiency requirements
- US Department of Energy: Monitoring data center growth
- State regulations: Some states considering data center power caps
- Carbon taxes: Potential future costs for high-energy AI operations
The enterprise AI technology sector may face increasing environmental compliance requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 How much power does the OpenAI Broadcom deal involve?
The OpenAI Broadcom partnership will deploy 10 gigawatts of custom AI chips and systems, equivalent to the electricity consumption of approximately 8 million US households or a large metropolitan city. This massive computing capacity is needed to support ChatGPT’s 800 million weekly users and the rapidly growing Sora 2 video generation platform.
When will OpenAI start using Broadcom’s custom AI chips?
Deployment of the custom AI accelerator and network systems is expected to begin in the second half of 2026. The design and development phase is currently underway, with full-scale implementation projected for 2027-2028 as OpenAI continues expanding its AI infrastructure.
Why does Sora 2 use so much more power than ChatGPT?
Sora 2 video generation requires 50-100 times more computational power than ChatGPT text queries. Generating realistic 10-second videos involves processing thousands of individual frames, complex motion calculations, and high-resolution rendering—all of which demand significantly more energy than simple text generation.
How did Broadcom stock react to the OpenAI partnership announcement?
Broadcom shares surged 12% on Monday morning following the announcement, adding over $140 billion to the company’s market capitalization. The deal, worth an estimated $10-15 billion, was seen by investors as validation of Broadcom’s AI chip strategy and a major competitive win against rivals.
What is the environmental impact of AI data centers consuming this much power?
According to a 2024 Department of Energy report, data center energy usage is expected to grow from 4.4% of total US electricity in 2023 to potentially 12% by 2028. The environmental impact depends on energy sources—if powered by coal, 10 gigawatts could produce 50+ million tons of CO₂ annually, but renewable energy sources could reduce this to under 1 million tons.
Conclusion: The High Cost of AI’s Next Evolution
The OpenAI Broadcom deal represents far more than a simple chip partnership. It’s a stark illustration of AI’s enormous appetite for computing power and the infrastructure investments required to sustain this technology’s growth.
As ChatGPT serves 800 million weekly users and Sora 2 grows even faster, the demand for electricity will only increase. The 10-gigawatt agreement—enough to power a major city—may be just the beginning.
Key takeaways:
✅ Custom AI chips will give OpenAI greater control and efficiency
✅ Power consumption is becoming AI’s biggest scalability challenge
✅ Environmental concerns will drive innovation in energy-efficient computing
✅ The semiconductor industry is experiencing an AI-driven boom
✅ Regulatory oversight of data center energy usage is likely coming
What’s next? Watch for competing announcements from Google, Meta, and Amazon as the race for AI computing supremacy intensifies.
BLOG – Why Nvidia Is at the Center of the Explosive US-China Trade War Over AI Chips


